
When buying a car, one of the biggest decisions you’ll face is choosing between AWD (All-Wheel Drive) and 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive). Both systems are designed to improve traction, but they work in different ways and are best suited for different driving conditions. Whether you’re navigating icy roads, rugged trails, or just driving through the city, understanding these systems can help you make a smarter choice.
This guide breaks down the key differences between AWD and 4WD, explains how they work, and highlights their pros and cons. By the end, you’ll know which one suits your driving lifestyle.
What Is AWD (All-Wheel Drive)?

All-Wheel Drive, or AWD, is a system that automatically powers all four wheels of your vehicle. Unlike front-wheel or rear-wheel drive cars, AWD distributes power to all wheels as needed to give you better grip, especially on slippery roads.
How Does AWD Work?
AWD uses a center differential or an electronically controlled clutch to split power between the front and rear wheels. It monitors road conditions in real-time and adjusts power automatically, so you don’t have to do anything. Some advanced systems even send more torque to specific wheels to ensure maximum traction.
Types of AWD Systems
- Full-Time AWD:
- Always on and constantly powering all four wheels.
- Great for people driving in areas with frequent rain, snow, or gravel roads.
- Part-Time AWD:
- Works as front- or rear-wheel drive under normal conditions.
- Activates all four wheels only when extra traction is needed, like in slippery situations.
Advantages of AWD
- Improved Traction: Ideal for wet roads, snow, and uneven surfaces.
- Convenience: Fully automated and doesn’t require driver input.
- Better Fuel Efficiency: More efficient than 4WD in most situations.
- Smooth Ride: Designed for on-road performance, making city driving more comfortable.
Disadvantages of AWD
- Tire Wear: Continuous power distribution can cause faster tire wear.
- Limited Off-Road Use: Not rugged enough for extreme terrains like deep mud or steep hills.
- Higher Cost: AWD vehicles tend to be more expensive.
Also Read: Child Car Seat Safety: A Complete Guide for Parents
What is 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive)?
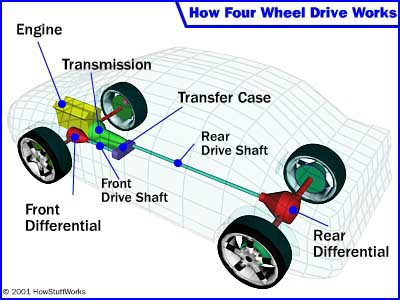
Four-Wheel Drive, or 4WD, is built for extreme off-road adventures. It’s designed to handle rugged terrains, deep mud, and steep inclines where maximum traction is essential.
How Does 4WD Work?
4WD sends power to all four wheels simultaneously, usually through a transfer case that splits power between the front and rear axles. Most systems require the driver to engage 4WD manually, although some advanced systems can switch automatically.
Types of 4WD Systems
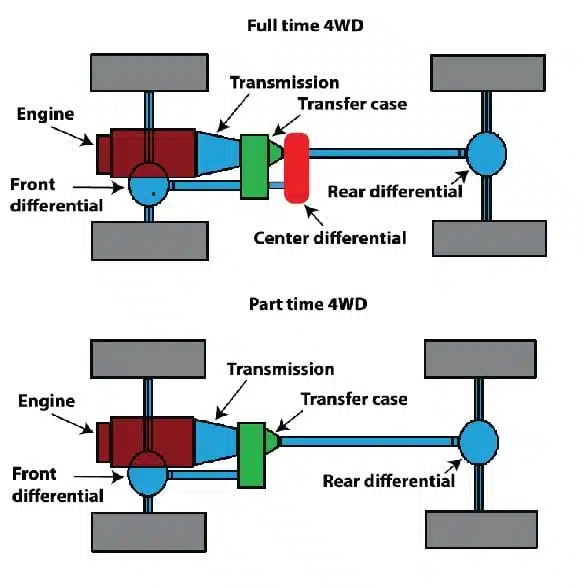
- Part-Time 4WD:
- Operates as two-wheel drive in normal conditions.
- The driver manually activates 4WD when needed for tougher terrain.
- Full-Time 4WD:
- Often found in high-performance off-road vehicles.
- Always powers all four wheels.
Some 4WD systems also include low-range gearing, which provides extra torque at low speeds for crawling over rocks or through deep snow.
Advantages of 4WD
- Superior Off-Road Capability: Perfect for challenging terrains like sand, mud, or rocks.
- Extreme Traction: Performs better than AWD in tough conditions.
- Low-Range Gearing: Offers extra power for steep climbs or deep ruts.
- Driver Control: Gives you the option to engage or disengage 4WD as needed.
Disadvantages of 4WD
- Fuel Efficiency: Less efficient than AWD due to heavier components.
- Cost: Generally more expensive to buy and maintain.
- Rough Ride: Not as smooth on paved roads.
Key Differences Between AWD and 4WD
| Feature | AWD (All-Wheel Drive) | 4WD (Four-Wheel Drive) |
| Primary Use | On-road driving with occasional light off-road conditions | Off-road driving, rugged terrains, and extreme weather |
| Power Distribution | Power automatically distributed to all four wheels as needed | Power distributed to all four wheels, often manually engaged |
| System Activation | Always on, no driver intervention required | Manual activation (or automatic on some systems) |
| Traction Control | Best for slippery roads, rain, snow, gravel | Best for deep mud, sand, snow, and rocky terrain |
| Fuel Efficiency | More fuel-efficient, as it uses fewer mechanical components | Less fuel-efficient due to additional drivetrain components |
| Off-Road Capability | Limited off-road capabilities, suitable for light off-roading | Superior off-road capabilities, handles tough terrains |
| Ride Quality | Smoother ride on paved roads, ideal for urban driving | Rougher ride, designed for off-road stability and control |
| Cost | Less expensive to maintain and purchase | Generally more expensive due to complex drivetrain |
| Low-Range Gearing | No low-range gearing available | Often includes low-range gearing for crawling over obstacles |
| Common Use | Found in sedans, crossovers, and light SUVs | Found in trucks, SUVs, and vehicles designed for off-roading |
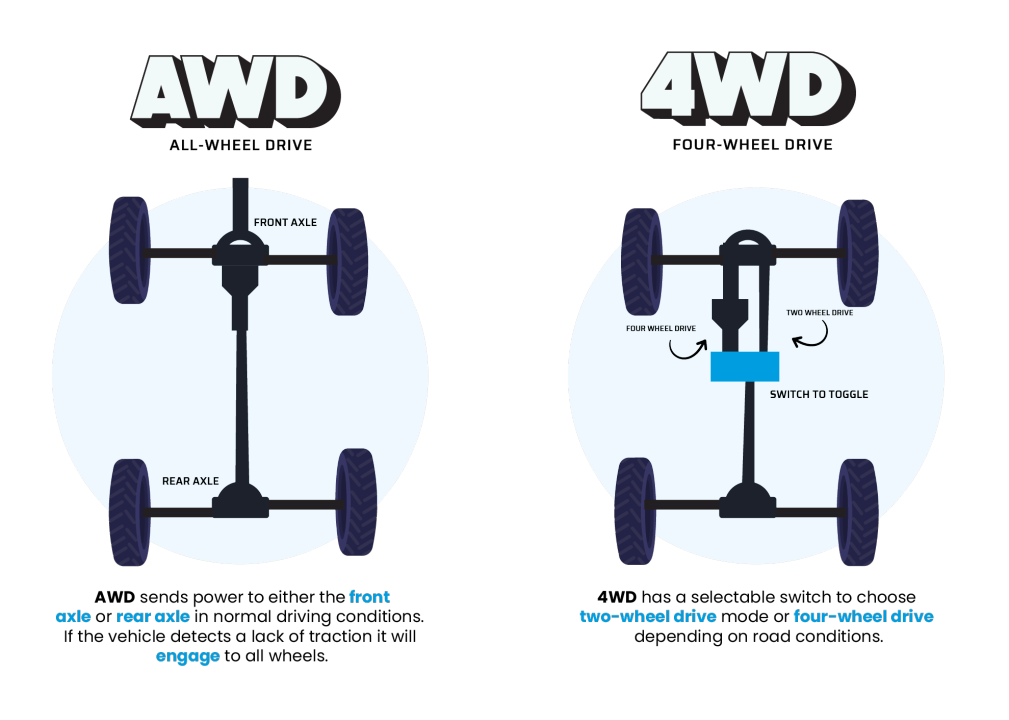
1. Purpose and Use
AWD is intended for vehicles that run on paved roads most of the time but sometimes find themselves on slippery or rough roads like wet roads, snow, or gravel. It improves on-road performance and stability.
4WD, on the other hand, is engineered for extreme off-road driving conditions. Its intention is to traverse extreme road conditions such as mud, sand, and rocks and to deliver better grip and control.
2. Automatic vs. Manual Engagement
AWD is usually always on and runs automatically without the intervention of the driver.
4WD is usually operated manually (though some systems allow automatic activation) and is engaged when more traction is needed.
3. Off-Roading Capability
AWD is not ideal for heavy off-roading, though it can handle light off-road conditions and slippery roads.
4WD is ideal for off-roading, as it offers better traction, low-range gearing, and more control in challenging conditions.
4. Fuel Efficiency
AWD is, in general, more fuel-efficient because they are not based on the massive heavy-duty parts needed in the 4WD.
Due to additional mechanical components, and power needed for it to propel all the wheels, 4WD generally have less fuel efficiency.
5. Cost and Complexity
Being fewer in specialized parts, the AWD is cost-effective and also easier to manufacture than a 4WD.
4WD vehicles tend to be more costly, as the additional expense is a more sophisticated drivetrain system meant for extreme conditions.
6. Ride and Handling
AWD will have a smoother ride on asphalt highways and handle better in everyday driving situations.
4WD systems make the ride less smooth and are suited better for off-road conditions than for smooth highways.
Also Read: Benefits of Regular Wheel Alignment: Why It’s Essential for Your Vehicle’s Performance and Longevity
Which System is Right for You?
The choice between AWD and 4WD depends on your driving needs:
You’re willing to trade some fuel efficiency for off-road performance.
Choose AWD if:
- You mostly drive on paved roads but occasionally face rain, snow, or light off-road conditions.
- You want a convenient system that doesn’t require manual activation.
- You prioritize fuel efficiency and a smooth ride.
Choose 4WD if:
- You’re an off-road enthusiast or live in an area with extreme weather and rugged terrain.
- You need maximum traction and control in challenging conditions.
What’s the main difference between AWD and 4WD?
AWD automatically adjusts power to all four wheels, while 4WD is usually manually engaged and designed for extreme off-road use.
Which is better for snow: AWD or 4WD?
AWD is better for light snow and icy roads, while 4WD is ideal for deep snow and off-road conditions.
Is 4WD harder to maintain than AWD?
Yes, 4WD systems are more complex and usually require more maintenance than AWD systems.
Conclusion
Both AWD and 4WD have their strengths and weaknesses. AWD offers convenience and comfort for everyday driving, while 4WD provides unmatched off-road capability. By understanding your driving needs and the environments you’ll face, you can choose the system that’s right for you. Whether it’s tackling snowy streets or climbing rocky trails, the right drivetrain can make all the difference.